What is Cardano (ADA)? The Complete Guide to the Blockchain, Ecosystem, and Governance

- What is ADA? A third-generation blockchain offering scalability and sustainability improvements over Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Key Features: Peer-reviewed research, Ouroboros PoS protocol, liquid staking.
- Governance: Decentralized through Voltaire, enabling community voting.
- Ecosystem: Multi-layered architecture, smart contracts, and a vibrant community.
Introduction
1.What is Cardano (ADA)? Understanding the Blockchain
The Ecosystem of Cardano
- Ouroboros Protocol: The backbone of Cardano’s security, this PoS protocol allows for greater scalability and sustainability.
- Two-Layer System (CSL and CCL): The settlement layer (CSL) handles ADA transactions, while the computation layer (CCL) runs smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).
- Decentralization: Cardano is committed to decentralization through Shelley, one of its key phases, which introduced staking and allowed for a more decentralized network.

2.The Origin and Evolution of Cardano (ADA)
- Byron Era (Foundation): The initial launch of Cardano, including the creation of the ADA token.
- Shelley Era (Decentralization): The introduction of staking, which decentralized the network and introduced Cardano's PoS mechanism.
- Goguen Era (Smart Contracts): Enabling the development of decentralized applications (dApps) on the Cardano blockchain.
- Basho Era (Scalability): Focused on optimizing scalability, particularly through the Hydra upgrade.
- Voltaire Era (Governance): Empowering the community with governance tools to vote on proposals and changes to the protocol.
3.Cardano’s Technological Framework: How Cardano Works
Two-Layer Architecture: CSL and CCL
- CSL: Handles ADA transactions and acts as the ledger for the blockchain.
- CCL: Focuses on running smart contracts and decentralized applications.
4.Cardano’s Staking and ADA Token
Benefits of Liquid Staking
- Flexibility: Users can stake their tokens while still having the freedom to move or sell them.
- Security: Staking helps secure the network, ensuring that the blockchain operates smoothly and securely.
- Rewards: Stakers earn rewards for participating in securing the network.

5.Cardano’s Governance: Decentralized Decision Making

6.The Challenges and Criticisms of Cardano
- Slow Development: Cardano’s academic approach leads to slower development compared to other blockchains like Ethereum.
- Adoption Issues: Although Cardano is widely regarded for its academic rigor and theoretical strength, real-world adoption and application are still growing.
7.Cardano’s Ecosystem: Wallets, dApps, and More
- Daedalus: A full-node wallet that provides users with full control of their funds.
- Yoroi: A lightweight wallet for fast and easy access to Cardano.
8.FAQ Section
9.Conclusion
Popular Articles

Who is Charles Hoskinson? Cardano Founder Background & Vision
Charles Hoskinson is a prominent figure in the cryptocurrency space, best known as the co-founder of Ethereum and the founder of Cardano. Hoskinson has played a significant role in shaping the future

Cardano vs Solana: Key Differences in Architecture & Design Philosophy
When it comes to blockchain technology, two projects often discussed in the same breath are Cardano (ADA) and Solana (SOL). Both are third-generation blockchains designed to address the scalability an

Cardano Price Analysis: Understanding ADA's Market Cap & Price Potential
As Cardano’s ADA continues to grow in the crypto space, one question often arises: Can ADA reach $10? While thecryptocurrency market is known for its volatility, understanding market cap and price pre

The Rise of CommerceFi: Why Crypto Payments Are Going Mainstream
Crypto cycles are predictable. A new infrastructure wave arrives. Liquidity pours into Layer 1 ecosystems. A token meta monopolizes attention. Eventually the narrative burns out and the market looks f
Hot Crypto Updates
View More
Cardano (ADA) Latest Price: Fresh Market Updates
The crypto market changes minute by minute, and the latest Cardano (ADA) price offers the most up-to-date snapshot of its value. In this article, we highlight the newest movements, fresh data from

Cardano (ADA) Bullish Price Prediction
Introduction to Bullish ADA Outlook Optimistic investors often look to bullish price predictions for Cardano (ADA) to identify the coin's growth potential during favorable market cycles. A bullish

Cardano (ADA) Price Prediction: Market Forecast and Analysis
Understanding the price prediction of Cardano (ADA) gives traders and investors a forward-looking perspective on potential market trends. Cardano price predictions aren't guarantees, but they provide

Cardano (ADA) 7-day Price Change
The latest Cardano (ADA) price has shown significant movement over the past week. In this article, we'll examine its current price, 7-day performance, and the market factors shaping ADA's trend.
Trending News
View More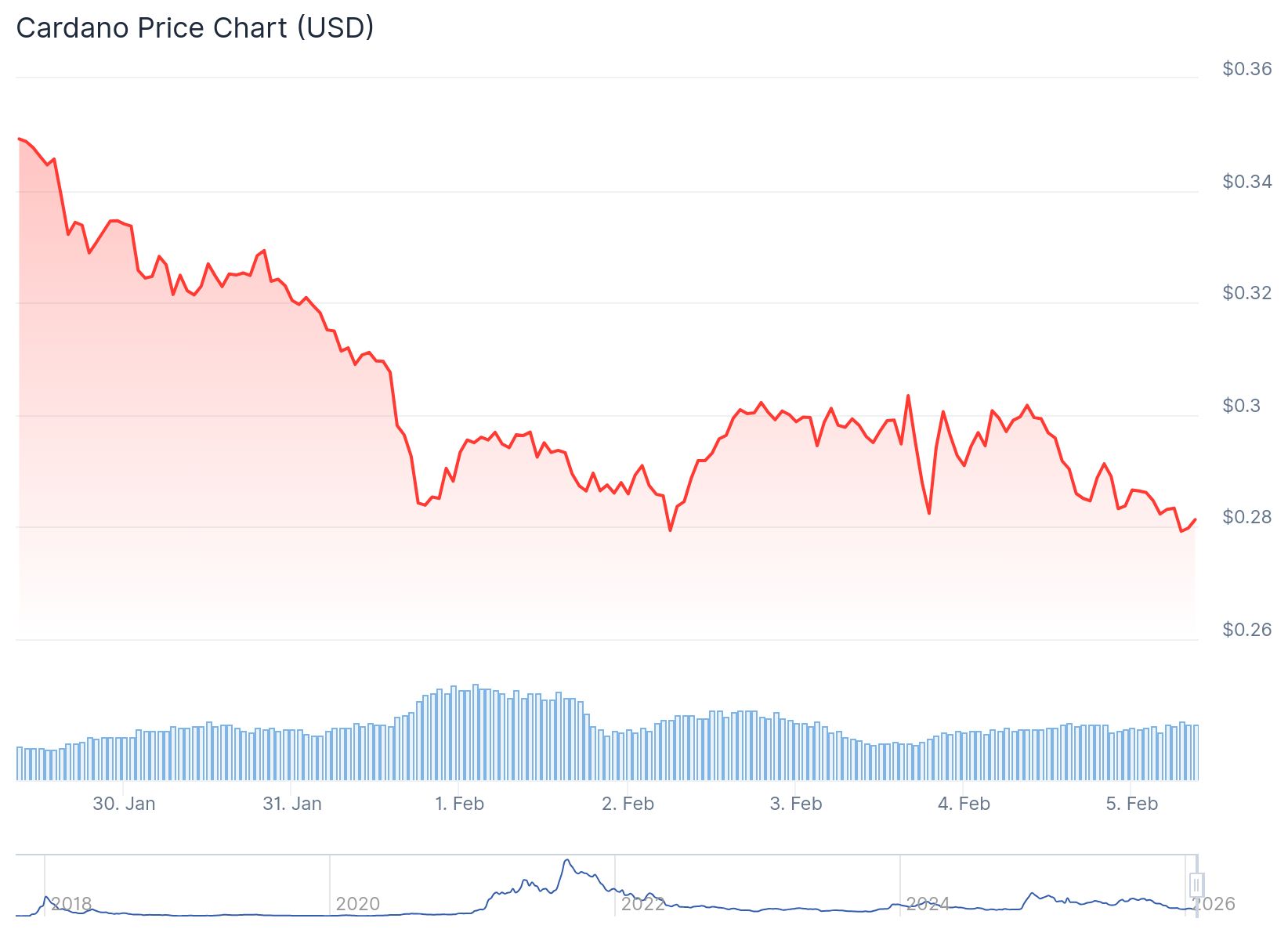
Cardano (ADA) Price: Market Correction Deepens as Support Levels Break Down
TLDR Cardano trades at $0.28 on Thursday, down more than 15% last week and approaching October 2023 lows Open interest at Binance dropped to $90.21 million, the

Cardano Founder Unveils Logan Update: 8 Powerful New Integrations Explained
Cardano founder Charles Hoskinson has unveiled an update for the Logan AI agent, adding token analytics and a blockchain explorer. Other upgrades include CSWAP,

Cardano Founder Announces 32 New Tools, ADA Drops Out of Top 1
Cardano’s ADA has dropped out of the top 10 cryptocurrencies following a sharp selloff as Hoskinson announced a major Logan AI upgrade. The post Cardano Founder

ADA Price Prediction: Oversold Cardano Targets $0.31-$0.35 Recovery by March 2026
ADA trades at $0.28 with RSI at 29.48 signaling oversold conditions. Technical analysis suggests potential bounce to $0.31-$0.35 range within 4 weeks as momentum
Related Articles

Who is Charles Hoskinson? Cardano Founder Background & Vision
Charles Hoskinson is a prominent figure in the cryptocurrency space, best known as the co-founder of Ethereum and the founder of Cardano. Hoskinson has played a significant role in shaping the future

Cardano vs Solana: Key Differences in Architecture & Design Philosophy
When it comes to blockchain technology, two projects often discussed in the same breath are Cardano (ADA) and Solana (SOL). Both are third-generation blockchains designed to address the scalability an

Cardano Price Analysis: Understanding ADA's Market Cap & Price Potential
As Cardano’s ADA continues to grow in the crypto space, one question often arises: Can ADA reach $10? While thecryptocurrency market is known for its volatility, understanding market cap and price pre

The Rise of CommerceFi: Why Crypto Payments Are Going Mainstream
Crypto cycles are predictable. A new infrastructure wave arrives. Liquidity pours into Layer 1 ecosystems. A token meta monopolizes attention. Eventually the narrative burns out and the market looks f
