In-depth analysis of Loopscale: How to restructure the Solana DeFi lending market?
Loopscale: Order book lending on Solana
Author: Castle Labs
Compiled by: Luiza, ChainCatcher
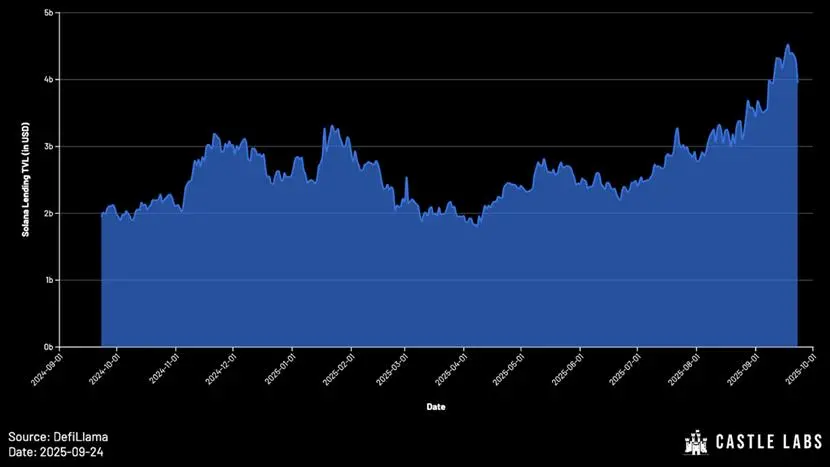
While Ethereum’s DeFi total value locked (TVL) is still far from its 2021 peak, Solana’s TVL has seen significant growth and is now at a new all-time high.
The characteristics of the Solana ecosystem make it an ideal choice for lending protocols. This is evident in protocols like Solend, which already boasted nearly $1 billion in deposits in 2021. While the FTX debacle severely impacted the development of the Solana lending ecosystem in the years that followed, lending protocols on Solana have demonstrated significant resilience, spurring a new wave of growth.
In 2024, the TVL of Solana’s on-chain lending protocols was less than $1 billion. Today, that figure has exceeded $4 billion. Kamino leads with over $3 billion in TVL, followed by Jupiter with $750 million in TVL.
This study will first analyze the limitations of pool-based lending models and the rise of alternative models. It will then delve into Loopscale's value proposition, unique features, and the practical benefits it brings to users. Finally, it will explore future trends in the lending market and raise several questions worth considering.
The evolution of lending models
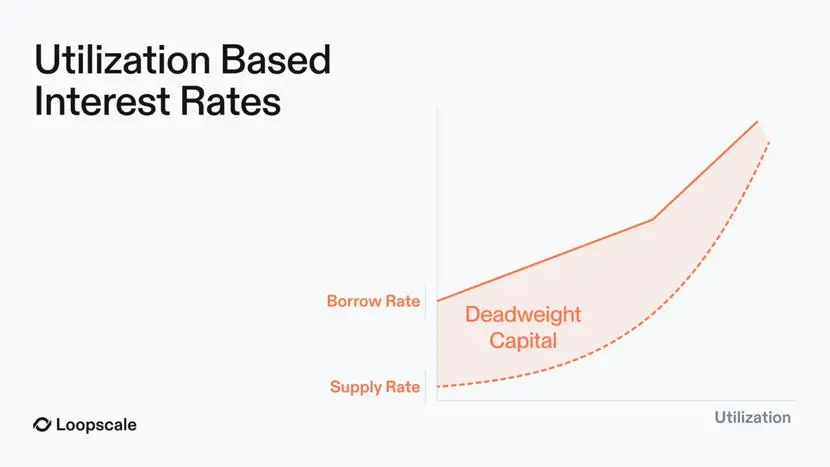
Mainstream lending protocols (such as Aave and Compound) generally adopt a pool model: users inject liquidity into the pool, which is then used by others to borrow. The interest rate is dynamically adjusted by an algorithm based on the utilization rate of funds (total borrowing amount divided by total deposit amount).
In the early days, the flexibility of this type of protocol design was limited by the limitations of the Ethereum mainnet architecture. Although the fund pool model has advantages in the startup phase and in ensuring the liquidity of collateral assets, it has obvious shortcomings:
- Liquidity fragmentation (difficulties in listing new assets): Each new asset requires a separate fund pool, which inevitably leads to liquidity fragmentation. It also makes it more complex for users to manage multiple positions, requiring more active management efforts.
- Rough risk pricing: The utilization curve is an inefficient, one-size-fits-all pricing mechanism that can ultimately lead to either overly aggressive terms (excessively high risk) or overly conservative terms (excessively low returns). In effect, the interest rate on the pool tends to align with the riskiest collateral in the pool.
- Inefficient capital utilization: In a pooled lending market, only borrowed funds accrue interest, but this interest income must be distributed to all depositors. This means that the actual interest earned by lenders is lower than the interest paid by borrowers, resulting in "deadweight capital." Furthermore, idle funds in the pool awaiting lending also participate in the interest distribution, further widening the aforementioned interest rate spread.
To alleviate these problems, protocols such as Euler, Kamino (V2), and Morpho (V1) introduced curated vaults, where professional managers allocate funds and set interest rates.
This pragmatic improvement allows for a transformation without requiring a complete restructuring of the lending protocol's technology stack, while also addressing some of the issues with the pool model. In the Selected Vault model, vaults are managed by screened curators with specialized research and risk control capabilities, responsible for capital allocation, market selection, interest rate setting, and loan structure design. This model offers the following advantages to users:
- Users can choose different vault managers independently. Each vault is designed for specific risk preferences, so users do not need to be exposed to the risks of all assets supported by the fund pool.
- Easier portfolio management: Managers can quickly allocate assets to new markets, thereby more efficiently directing liquidity to new assets and facilitating the launch of new asset pools.
However, there are drawbacks to the Select Vault:
Trust and interest alignment issues: The vault is operated by a third-party manager, and users need to trust them. Moreover, the alignment of interests between managers and users is difficult to fully guarantee.
Manager Competition and Rising Borrower Costs: Managers are responsible for setting risk parameters, developing strategies, and adjusting liquidity in pursuit of higher returns. This liquidity adjustment process creates competition among managers' different strategies, which negatively impacts borrowers. Managers are incentivized to maintain high capital utilization rates to provide lenders with attractive annualized percentage yields (APYs), which in turn drives up borrowing rates and increases borrower costs.
The inherent flaws of the fund pool that the Selected Vault fails to address:
- The “value loss” caused by inefficient interest rates will still damage the capital efficiency of the lending market;
- Startup costs in new markets remain high;
- Liquidity remains fragmented across multiple independent markets;
- Interest rates are highly volatile, making it difficult to meet the needs of institutional users;
- Lack of flexibility: supporting new assets or credit products requires governance voting and the creation of new independent funding pools.
While Selected Vaults optimize risk management by splitting liquidity, they are still essentially a variation of the pool model. As the number of supported assets and risk profiles continues to expand, the logic behind Selected Vaults has become closer to that of an order book model—each borrowing and lending quote is a "separate market" with specific terms, achieving extreme sophistication.
Why is the order book model rising now?
Although the concept of order book lending has long been recognized, in the past, due to the high transaction costs and technical limitations of networks such as Ethereum, the deployment of order book models was often impractical and had obvious flaws in scalability and capital efficiency.
The rise of alternative public chains such as Solana has changed this situation - their low transaction costs and high throughput characteristics have finally made it possible to build a scalable and efficient order book lending market.
While the pool model has supported the scalability of lending protocols, the order book model provides much-needed flexibility, particularly for institutional users and diverse asset types such as interest-bearing RWA tokens (like OnRe’s ONyc), AMM LP positions, JLP/MLP tokens, and LSTs (with a TVL exceeding $7 billion), giving users full control over their risk profile.
Loopscale: An order-book lending protocol on the Solana chain
Loopscale is an order book-based lending protocol on the Solana chain. Its deposit liquidity currently exceeds US$100 million and its active loan scale reaches US$40 million.
Unlike traditional lending platforms based on capital pools, Loopscale's core innovation is that it allows lenders to create customized orders and independently set loan structures and risk parameters. These quotes will be "listed" in the order book based on interest rates and other terms, and Loopscale's matching engine will complete the loan matching.
The core advantages of Loopscale's order book model
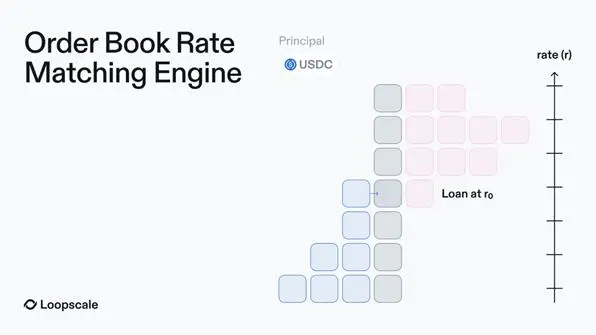
①Automated vault:
For users seeking further operational simplicity, Loopscale automates the process through its curated vaults. Liquidity injected into these vaults is available across all manager-approved markets, and each vault is staffed by a risk manager with unique risk appetite and strategies.
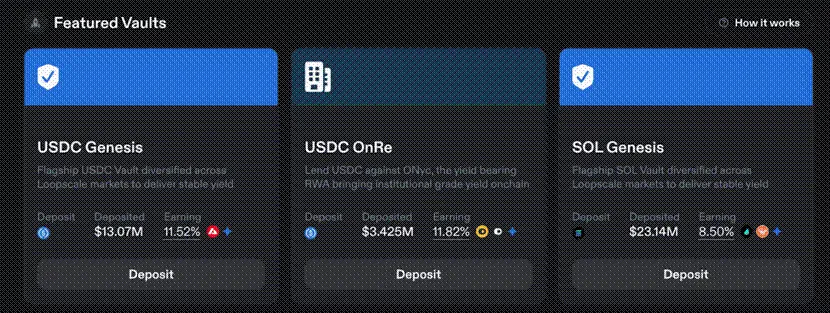
This design forms a differentiated strategy system that can meet the risk needs of different users: for example, some users may be willing to assume reinsurance-related risks (through ONyc tokens) through the USDC OnRe vault; while users with more conservative risk preferences can choose to deposit funds in the USDC Genesis vault - which will provide robust liquidity diversification across Loopscale markets.
②One-key cycle leverage:
In addition to traditional lending, Loopscale also supports a "funding loop" feature. Through this feature, users can leverage interest-bearing assets (including JLP, ALP, digitSOL, ONyc, etc.). The specific principles are as follows:
The core logic of the capital cycle is: after depositing collateral assets, the same assets as the collateral are borrowed, so that both the initial holdings and the borrowed tokens can generate returns. The leverage multiple that users can obtain depends on the market's loan-to-value ratio (LTV).
Taking Liquidity Staking Token (LST) as an example, the traditional capital circulation process is as follows:
1. Deposit wstETH (wrapped staked ETH);
2. Borrow ETH;
3. Exchange ETH to wstETH;
4. Borrow ETH again to obtain higher wstETH returns.
It should be noted that the capital circulation operation will only have actual benefits when the LST yield is higher than the annualized loan interest rate.
On Loopscale, this process is simplified to a "one-click operation", and users do not need to complete multiple steps manually.
Through the fund circulation function, users can maximize the APR of interest-bearing tokens;
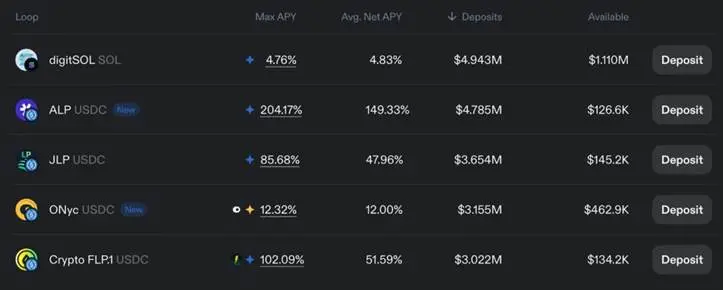
In addition, leveraged funding cycles also allow users to conduct directional leveraged trading on assets such as stocks.
③Solutions to the defects of the fund pool model
Liquidity Aggregation
The order book model addresses the fragmented liquidity issues in the pooled market. Loopscale further addresses the fragmented liquidity of the pooled market and the difficulty in reusing funds in the earlier order book model by creating a "virtual market." Lenders can place orders simultaneously across multiple markets with a single operation, without being restricted to a single market or managing multiple positions.
Efficient pricing
Each market on Loopscale is modular, with its own unique collateral type, lending rate, and terms. This means lenders can set interest rates based on specific collateral and principal, regardless of capital utilization. Ultimately, the interest rate for each asset adjusts dynamically based on market supply and demand in the order book (which may be influenced by factors such as asset volatility).
This design simultaneously achieves the following goals: minimizing “ineffective funds”; ensuring that borrowing rates are fully aligned with deposit rates (in a pooled funding model, interest income is distributed to all depositors, resulting in lenders’ returns being lower than borrowers’ costs; on Loopscale, interest is only paid on funds that are actually utilized, achieving precise interest rate matching);
In particular, it supports fixed-rate, fixed-term loans to meet the needs of institutional users, who are generally reluctant to accept interest rates based on utilization fluctuations in the funding pool model.
Optimize capital utilization
Loopscale uses its "yield optimization" mechanism to reduce the amount of idle funds in the order book waiting to be matched. The operating logic is simple and straightforward: Loopscale directs this idle liquidity to the MarginFi platform, ensuring that lenders can still "earn a competitive yield" until their orders are matched.
Expanding the scope of asset support
The Loopscale team can easily integrate with other protocols and take full advantage of Solana's asset composability to support assets that have difficulty obtaining liquidity in the pool market.
④ Actual benefits for users
These features bring tangible benefits to users: users have complete control over loan terms, collateral assets, and participating markets, enabling refined management. As competition in the lending market intensifies at the interest rate level, the Loopscale model has advantages over pricing methods based on fund pool utilization. By directly matching orders, interest rates can be precisely aligned, saving costs for borrowers and increasing returns for lenders.
Future Outlook and Conclusion
Loopscale addresses the inefficiencies of the pool model by combining the flexibility of order books with modular markets, providing users with customized interest rates, optimized collateral pricing, and risk management tools.
As DeFi expands to include institutional capital and RWAs, the order book model will become a critical infrastructure for scaling on-chain lending. Loopscale already supports a variety of RWAs and exotic assets and continues to expand its partnerships. Adding new markets only requires an oracle and initial liquidity (which can be provided by vaults or individual lenders), significantly lowering the barrier to entry.
The Solana ecosystem is currently benefiting from widespread adoption of new token prototypes, including billions of dollars worth of LST, Liquidity-Backed Derivatives (LRT), staked SOL (which now accounts for 60% of the total SOL supply), Liquidity Positions, and Reliable Token Assets (RWAs). In this context, lowering the barrier to entry for new assets as collateral is key to improving market efficiency. The viability of the order book lending model has been widely recognized by the market—protocols like Morpho have already launched similar designs in their V2 releases.
Although Loopscale suffered a hack in April 2025 (shortly after its launch), the team demonstrated strong resilience and all funds were recovered. It's important to note that handling complex collateral carries inherent risks, requiring thorough risk assessment and management at both the operational and user interface levels. By effectively addressing these challenges, Loopscale is poised to leverage Solana's technology stack to optimize its architecture and successfully scale the platform.
You May Also Like

How to earn from cloud mining: IeByte’s upgraded auto-cloud mining platform unlocks genuine passive earnings

RFK Jr. reveals puzzling reason why he loves working for Trump
