Here's What You Need to Know About Vulnerability Management for Go
We are excited to announce Go’s new support for vulnerability management, our first step towards helping Go developers learn about known vulnerabilities that may affect them.
\ This post provides an overview of what’s available today and next steps for this project.
Overview
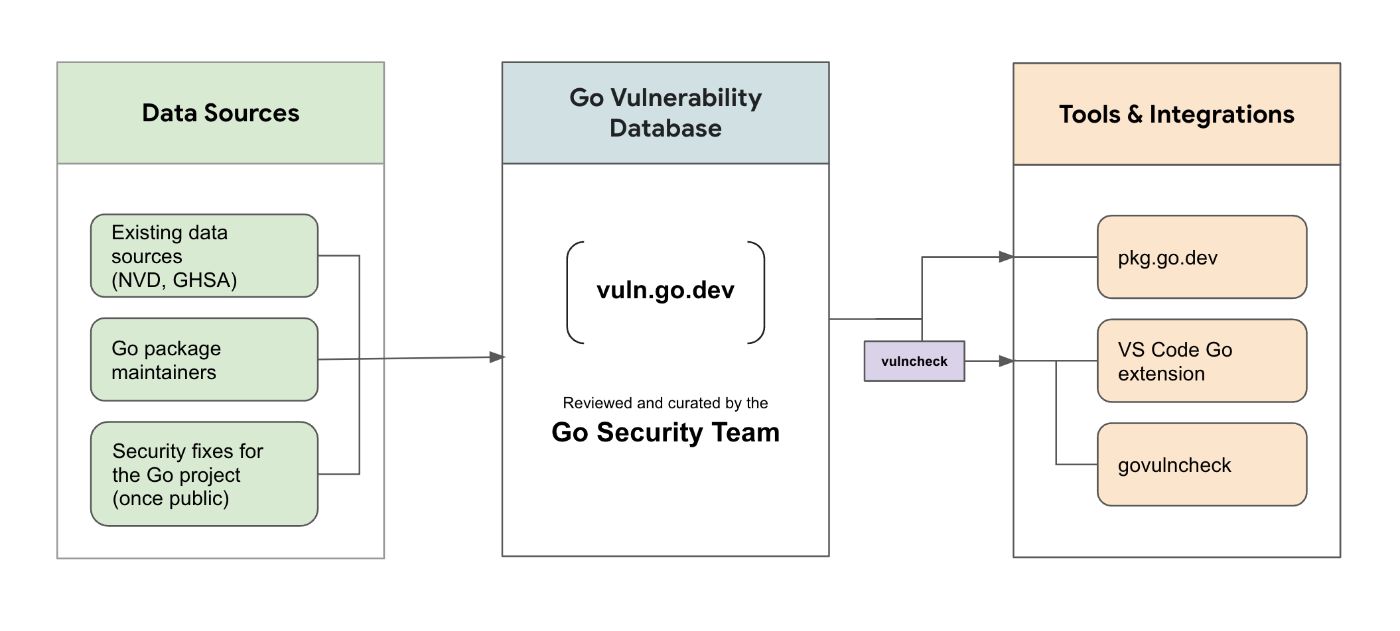
Go provides tooling to analyze your codebase and surface known vulnerabilities. This tooling is backed by the Go vulnerability database, which is curated by the Go security team. Go’s tooling reduces noise in your results by only surfacing vulnerabilities in functions that your code is actually calling.
\
Go vulnerability database
The Go vulnerability database (https://vuln.go.dev) is a comprehensive source of information about known vulnerabilities in importable packages in public Go modules.
\ Vulnerability data comes from existing sources (such as CVEs and GHSAs) and direct reports from Go package maintainers. This information is then reviewed by the Go security team and added to the database.
\ We encourage package maintainers to contribute information about public vulnerabilities in their own projects and update existing information about vulnerabilities in their Go packages. We aim to make reporting a low friction process, so please send us your suggestions for any improvements.
\ The Go vulnerability database can be viewed in your browser at pkg.go.dev/vuln. For more information about the database, see go.dev/security/vuln/database.
Vulnerability detection using govulncheck
The new govulncheck command is a low-noise, reliable way for Go users to learn about known vulnerabilities that may affect their projects. Govulncheck analyzes your codebase and only surfaces vulnerabilities that actually affect you, based on which functions in your code are transitively calling vulnerable functions.
\ You can install the latest version of govulncheck using go install:
$ go install golang.org/x/vuln/cmd/govulncheck@latest \ Then, run govulncheck inside your project directory:
$ govulncheck ./... Govulncheck is a standalone tool to allow frequent updates and rapid iteration while we gather feedback from users. In the long term, we plan to integrate the govulncheck tool into the main Go distribution.
Integrations
It’s always better to learn about vulnerabilities as early as possible in the development and deployment process. To integrate vulnerability checking into your own tools and processes, use govulncheck -json.
\ We have integrated vulnerability detection into existing Go tools and services, such as the Go package discovery site. For example, this page shows the known vulnerabilities in each version of golang.org/x/text. Vulnerability checking functionality through the VS Code Go extension is also coming soon.
Next Steps
We hope you’ll find Go’s support for vulnerability management useful and help us improve it!
\ Go’s support for vulnerability management is a new feature that is under active development. You should expect some bugs and limitations.
\ We would love for you to contribute and help us make improvements in the following ways:
- Contribute new and update existing information about public vulnerabilities for Go packages that you maintain
- Take this survey to share your experience using govulncheck
- Send us feedback about issues and feature requests
\ We are excited to work with you to build a better and more secure Go ecosystem.
Julie Qiu, for the Go security team
\ This article is available on The Go Blog under a CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
\ Photo by Growtika on Unsplash
คุณอาจชอบเช่นกัน

Aave DAO to Shut Down 50% of L2s While Doubling Down on GHO

The Role of Reference Points in Achieving Equilibrium Efficiency in Fair and Socially Just Economies
