DePIN operates at the intersection of blockchain technology and real-world physical infrastructure — and here’s how it works in practice.
A provider manages a physical asset, while middleware software handles the interaction between that asset and the blockchain. This software collects real-time data on the activity of each device or resource and transmits it to the decentralized network.
The blockchain protocol acts like an autonomous coordinator, distributing demand across providers and calculating token-based rewards based on their performance and contribution.
This structure incentivizes providers to make the most of their unused or underutilized resources — turning idle capacity into productive infrastructure.
DePIN projects generally fall into two broad categories:
- Physical Resource Networks (PRNs) – These rely heavily on geolocation and offer non-fungible resources tied to a specific place. Their services are usually localized and often relate to mobile technologies or energy systems.
- Digital Resource Networks (DRNs) – These provide computing power or storage space, and their resources are location-agnostic and interchangeable.
DePIN is already reshaping various industries, with notable use cases across:
- Wireless connectivity (Helium)
- Decentralized cloud storage (Arweave)
- Smart energy grids (Arcreen)
- Mobile data solutions (Dimo)
- Decentralized computing (Nunet)
- Mapping and geolocation services (Hivemapper)
- Healthcare data systems (Healthblocks)
Next, let’s take a closer look at some of the most prominent and successful DePIN projects in the space.
Filecoin
Filecoin is a decentralized data storage platform built on the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS). Launched as one of the earliest real-world applications of the DePIN concept, the idea behind Filecoin dates all the way back to 2014.
The system allows users to store their data across a distributed network by paying network miners for available storage space. But there’s a twist — pricing is dynamic and constantly shifting, as miners compete to offer the lowest rates. The more space a miner contributes, the higher their potential reward in the network’s native cryptocurrency, FIL.
This competitive model not only drives down storage costs for users but also incentivizes miners to maximize their available capacity.
As of March 8, 2024, FIL was trading at $10.09.
Helium
Helium is a decentralized wireless network designed to provide low-cost internet access — often more affordable than traditional providers in countries like the United States or Canada.
Data is transmitted through user-operated hotspots that utilize Helium LongFi technology. Miners who maintain these network nodes earn HNT tokens, while subscribers receive MOBILE tokens, which can be used to renew their data plans.
As of the time of writing, the Helium network boasts over 984,900 active hotspots across more than 170 countries, with the highest concentration found in the U.S. and parts of Europe.
Render
Render is a decentralized rendering platform that connects creators with unused GPU power across the network. Providers offer up their graphics processing units (GPUs) to support visual content creation — from animations to complex 3D scenes — and are rewarded in RENDER tokens for their contributions.
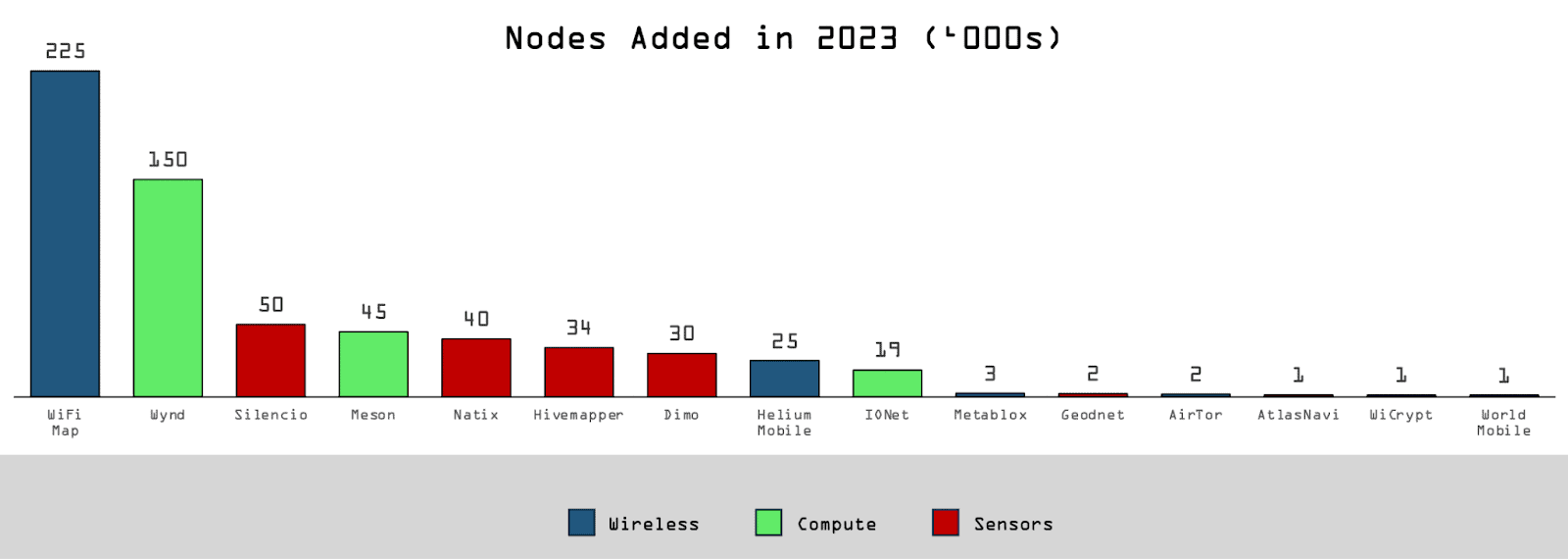 Number of New Nodes in DePIN Projects in 2023 Source: Messari.
Number of New Nodes in DePIN Projects in 2023 Source: Messari.

